Wayne County, Pennsylvania
Wayne County | |
|---|---|
 The Wayne County Courthouse in Honesdale | |
 Location within the U.S. state of Pennsylvania | |
 Pennsylvania's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 41°39′N 75°19′W / 41.65°N 75.31°W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | March 21, 1798 |
| Named for | Anthony Wayne |
| Seat | Honesdale |
| Largest borough | Honesdale |
| Area | |
• Total | 751 sq mi (1,950 km2) |
| • Land | 726 sq mi (1,880 km2) |
| • Water | 25 sq mi (60 km2) 3.3% |
| Population (2020) | |
• Total | 51,155 |
| • Density | 70/sq mi (30/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional district | 8th |
| Website | waynecountypa |
Wayne County is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. The county's population was 51,155 at the 2020 census.[1] The county seat is the Borough of Honesdale.[2] The county was formed from part of Northampton County on March 21, 1798,[3] and was named for the Revolutionary War General Anthony Wayne.[2] The county is part of the Northeast Pennsylvania and Pocono Mountains region of the state.[a]
The Lehigh River, a 109-mile-long (175 km) tributary of the Delaware River, begins in southern Wayne County.
Geography
[edit]According to the U.S. Census Bureau, Wayne County has a total area of 751 square miles (1,950 km2), of which 726 square miles (1,880 km2) is land and 25 square miles (65 km2) (3.3%) is water.[4]
The terrain of the county is varied. In the wider northern half, the land is rugged along its border with New York State, while the southern portion tends to be swampier. Higher hills and mountains are predominantly found along the county's western edge, while lower ones are more common in the east, near the Delaware River. The middle section of Wayne County is a wide plain.
The highest elevation in the county, 2,659 ft (810 m), is the summit of Mount Ararat in Orson. Two other summits at the north end of the same ridge also exceed 2,640 ft (800 m) in elevation. The county's lowest point, at approximately 680 ft (210 m) above sea level, is along the Delaware, near Wayne County's border with Pike County, Pennsylvania.
Most of Wayne County is drained by the Delaware (which separates Pennsylvania from New York), with the exception of a few small areas in the western part of the county, which are drained by either the Starrucca Creek or the Lackawanna River (which both eventually flow into the Susquehanna River).
The county has a warm-summer humid continental climate (Dfb) and average monthly temperatures in Honesdale range from 22.8 °F in January to 67.9 °F in July.[5]
Adjacent counties
[edit]- Broome County, New York (north)
- Delaware County, New York (northeast)
- Sullivan County, New York (east)
- Pike County (southeast)
- Monroe County (south)
- Lackawanna County (southwest)
- Susquehanna County (west)
Major highways
[edit]Demographics
[edit]| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1800 | 2,562 | — | |
| 1810 | 4,125 | 61.0% | |
| 1820 | 4,127 | 0.0% | |
| 1830 | 7,663 | 85.7% | |
| 1840 | 11,848 | 54.6% | |
| 1850 | 21,890 | 84.8% | |
| 1860 | 32,239 | 47.3% | |
| 1870 | 33,188 | 2.9% | |
| 1880 | 33,513 | 1.0% | |
| 1890 | 31,010 | −7.5% | |
| 1900 | 30,171 | −2.7% | |
| 1910 | 29,236 | −3.1% | |
| 1920 | 27,435 | −6.2% | |
| 1930 | 28,420 | 3.6% | |
| 1940 | 29,934 | 5.3% | |
| 1950 | 28,478 | −4.9% | |
| 1960 | 28,237 | −0.8% | |
| 1970 | 29,581 | 4.8% | |
| 1980 | 35,237 | 19.1% | |
| 1990 | 39,944 | 13.4% | |
| 2000 | 47,722 | 19.5% | |
| 2010 | 52,822 | 10.7% | |
| 2020 | 51,155 | −3.2% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census[6] 1790–1960[7] 1900–1990[8] 1990–2000[9] 2010–2017[10] 2010-2020[11] | |||
As of the Census of 2010, there were 52,822 people, 20,625 households, and 13,952 families in Wayne County. The county's population density was 72.797 people per square mile (28.107 people/km2), and there were 31,653 housing units at an average density of 43.623 per square mile (16.843/km2). The racial makeup of the populace was 94.2% White, 3.1% African American, 0.2% Native American, 0.5% Asian, 0.0% Pacific Islander, 0.9% of other races, and 1.1% of two or more races. Hispanics and Latinos of all races made up 3.4% of the population.[4][12]
67.6% of Wayne County's households were families, 53.9% were headed by a heterosexual married couple (Pennsylvania did not allow same-sex marriage until May 20, 2014, after the 2010 Census had been completed), and 26.6% included children under the age of 18. 9.2% of households were headed by a female householder with no husband present, 4.5% by a male householder with no wife present, and 32.4% consisted of non-families. 27.2% of all households were made up of individuals, and 12.3% consisted of a person 65 years of age or older living alone. The average household size was 2.38 and the average family size was 2.87.[12]
Wayne County's age distribution was 21.1% under the age of 18, 4.5% between the ages of 18 and 24, 23.1% between 25 and 44, 32.4% between 45 and 64, and 19.0% 65 years of age or older. The population's median age was 45.9 years. For every 100 females, there were 110 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 112 males in the same age range.[12]
According to American Community Survey (ACS) estimates, the median income for a household in Wayne County in 2013 was $49,313, and the median income for a family was $58,934. Males had a median income of $36,173, while females had a median income of $23,636. The per capita income for the county was $24,005. 8.4% of families and 12.2% of people were below the Census Bureau's poverty thresholds (different from the federally defined poverty guidelines), including 18.5% of those under age 18 and 7.6% of those age 65 or over.[13][14]
According to self-reported ancestry figures recorded by the ACS, the five largest ancestral groups in Wayne County in 2013 were Germans (30.3%), Irish (22.1%), Italians (13.9%), English (10.9%), and Poles (10.1%). Those reporting American ancestry made up 8.6% of the population.[15]
2020 census
[edit]| Race | Num. | Perc. |
|---|---|---|
| White (NH) | 44,821 | 87.62% |
| Black or African American (NH) | 1,647 | 3.22% |
| Native American (NH) | 73 | 0.14% |
| Asian (NH) | 418 | 0.82% |
| Pacific Islander (NH) | 0 | 0% |
| Other/Mixed (NH) | 1,849 | 3.61% |
| Hispanic or Latino | 2,347 | 4.6% |
Politics
[edit]| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third party(ies) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | |
| 2024 | 20,071 | 68.00% | 9,150 | 31.00% | 295 | 1.00% |
| 2020 | 18,637 | 66.21% | 9,191 | 32.65% | 319 | 1.13% |
| 2016 | 16,244 | 67.63% | 7,008 | 29.18% | 766 | 3.19% |
| 2012 | 12,896 | 59.50% | 8,396 | 38.74% | 382 | 1.76% |
| 2008 | 12,702 | 55.39% | 9,892 | 43.14% | 338 | 1.47% |
| 2004 | 13,713 | 62.43% | 8,060 | 36.69% | 194 | 0.88% |
| 2000 | 11,201 | 59.21% | 6,904 | 36.50% | 811 | 4.29% |
| 1996 | 8,077 | 49.45% | 5,928 | 36.29% | 2,329 | 14.26% |
| 1992 | 8,184 | 48.65% | 4,817 | 28.64% | 3,821 | 22.71% |
| 1988 | 9,926 | 71.61% | 3,775 | 27.23% | 161 | 1.16% |
| 1984 | 10,061 | 75.66% | 3,155 | 23.73% | 81 | 0.61% |
| 1980 | 8,468 | 67.48% | 3,375 | 26.90% | 705 | 5.62% |
| 1976 | 7,811 | 63.45% | 4,244 | 34.48% | 255 | 2.07% |
| 1972 | 8,948 | 74.51% | 2,733 | 22.76% | 328 | 2.73% |
| 1968 | 7,827 | 66.39% | 3,176 | 26.94% | 787 | 6.68% |
| 1964 | 6,512 | 52.82% | 5,781 | 46.89% | 35 | 0.28% |
| 1960 | 9,360 | 67.77% | 4,425 | 32.04% | 26 | 0.19% |
| 1956 | 9,658 | 75.64% | 3,092 | 24.22% | 18 | 0.14% |
| 1952 | 9,623 | 78.96% | 2,530 | 20.76% | 34 | 0.28% |
| 1948 | 7,708 | 77.14% | 2,284 | 22.86% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 1944 | 8,242 | 74.43% | 2,793 | 25.22% | 39 | 0.35% |
| 1940 | 9,203 | 72.44% | 3,460 | 27.24% | 41 | 0.32% |
| 1936 | 9,347 | 65.00% | 4,864 | 33.82% | 169 | 1.18% |
| 1932 | 6,215 | 61.47% | 3,666 | 36.26% | 230 | 2.27% |
| 1928 | 8,576 | 72.78% | 3,148 | 26.72% | 59 | 0.50% |
| 1924 | 5,578 | 72.87% | 1,477 | 19.29% | 600 | 7.84% |
| 1920 | 5,164 | 73.14% | 1,589 | 22.51% | 307 | 4.35% |
| 1916 | 2,869 | 55.84% | 2,019 | 39.30% | 250 | 4.87% |
| 1912 | 659 | 12.29% | 1,924 | 35.90% | 2,777 | 51.81% |
| 1908 | 3,650 | 56.67% | 2,438 | 37.85% | 353 | 5.48% |
| 1904 | 3,386 | 56.85% | 2,097 | 35.21% | 473 | 7.94% |
| 1900 | 3,229 | 50.91% | 2,647 | 41.74% | 466 | 7.35% |
| 1896 | 3,708 | 56.59% | 2,473 | 37.74% | 371 | 5.66% |
| 1892 | 2,690 | 44.41% | 2,915 | 48.13% | 452 | 7.46% |
| 1888 | 2,939 | 46.47% | 3,010 | 47.60% | 375 | 5.93% |
As of January 8, 2024, there were 35,181 registered voters in Wayne County, with the following party breakdown:[18]
- Republican: 20,299 (57.70%)
- Democratic: 9,134 (25.96%)
- Other: 1,119 (3.18%)
- Non-affiliated: 4,629 (13.16%)
Chart of Voter Registration
Wayne has long been one of the most Republican counties in Pennsylvania, as Republicans consistently win easily in federal, state and local elections. In 2000, Republican George W. Bush won 59.21 percent of the vote to Democrat Al Gore's 36.50 percent,[19] and in 2004, Bush won with 62.43 percent to Democrat John Kerry's 36.69 percent.[20] In 2008, Republican John McCain won with 55.39 percent of the vote to Democrat Barack Obama's 43.14 percent,[21] and in 2012, Republican Mitt Romney won with 59.50 percent to Obama's 38.74 percent.[22] In 2016, Republican Donald J. Trump won with 67.63 percent to Hillary Clinton's 29.18 percent.
Wayne County was one of the four counties that Barry Goldwater won in Pennsylvania in 1964;[23] the last Democrat to win a plurality in the county was Grover Cleveland in 1892.[24][25] Since then, only three Democrats have won even forty percent of the county's vote – William Jennings Bryan in 1900, Lyndon B. Johnson in 1964 and Barack H. Obama in 2008.
Government and infrastructure
[edit]United States senators
[edit]- John Fetterman (senior senator), Democrat
- Dave McCormick (junior senator), Republican
United States representative
[edit]- Rob Bresnahan, Republican (PA-8)
- Jonathan Fritz, Republican (111th district) - Buckingham, Clinton (partially), Lebanon, Manchester, Mount Pleasant, Oregon, Preston, and Scott Townships, and Starrucca Borough
- Vacant (139th district) - Berlin, Cherry Ridge, Clinton (partially), Damascus, Dyberry, Palmyra, Paupack, South Canaan, and Texas Townships, and Bethany, Hawley, Honesdale, and Prompton Boroughs
- Lisa Baker, Republican (20th district)
County commissioners
[edit]Other county officers
[edit]- Auditors:[28] Carla J. Komar, Republican; Kathy Schloesser, Democrat; Catherine Jane Rickard, Republican
- Coroner:[29] Edward R. Howell, Republican
- District Attorney:[30] A.G. Howell, Republican
- Prothonotary:[31] Edward "Ned" Sandercock, Republican
- Recorder of Deeds[32] and Register of Wills:[33] Debbie Bates, Republican
- Sheriff:[34] Christopher Rosler, Republican
- Treasurer:[35] Brian T. Field, Republican
Healthcare services
[edit]Wayne County is served by the Wayne Memorial Health System. The Health System consists of Wayne Memorial Hospital in Honesdale and several other subsidiaries and/or affiliates. In addition, the community has a number of physicians and other professionals providing needed care. The Farview State Hospital is located in Farview.
Emergency services
[edit]Paramedic services are provided by three different agencies:
- Wayne Ambulance, an affiliate of Lackawanna Ambulance (based in Scranton) which is owned by Community Health Systems, provides advanced life support and basic life support services to most of Wayne County, from a base in Honesdale.[36][37]
- Cottage Hose Company / Mobile 9, based in Carbondale, Lackawanna County, provides advanced life support to all of Wayne County, as well as basic life support as a mutual aid or private service. They primarily respond to calls in Waymart and South Canaan and Clinton Townships, as this area adjoins their primary service area. They also service Forest City, Pennsylvania, which is located in Susquehanna County but dispatched through Wayne County due to their coverage of Browndale.[38]
- Pike County Advanced Life Support / Mobile 401, has a sub-station in Hawley, provides Advanced Life Support services to a small western part of the Wayne County, including Hawley and Palmyra Township
BLS services are provided as dispatched through the Wayne County Communication Center. These agencies include:
- Damascus Township Volunteer Ambulance Corps, a volunteer ambulance corps, provides basic life support services in Damascus Township, along with 60% of Lebanon, 20% of Buckingham and all of Manchester township.
- Newfoundland Area Ambulance, a volunteer ambulance corps, provides basic life support services in Dreher Township, and portions of adjoining Sterling and Lehigh townships.
- Hawley Ambulance & Rescue Company provides BLS services.[39]
- White Mills Community Ambulance provides BLS services.[39]
- Northern Wayne Fire Company provides BLS service from their station on Route 370 in Lakewood.[40]
Maplewood Fire and Rescue provides QRS "quick response service" to all medical calls in Lake townships.
Prisons
[edit]The Federal Bureau of Prisons United States Penitentiary, Canaan is in Canaan Township, near Waymart.[41][42]
Education
[edit]
Public school districts
[edit]School districts include:[43]
- Forest City Regional (also in Lackawanna and Susquehanna)
- North Pocono (also in Lackawanna)
- Susquehanna Community (also in Susquehanna)
- Wallenpaupack Area (also in Pike)
- Wayne Highlands
- Western Wayne
Private schools
[edit]There are five private or parochial schools in Wayne County:
Libraries
[edit]The Wayne Library Alliance[46] operates seven public libraries throughout the county:
- The Bethany Public Library[47] in Bethany
- Hamlin Community Library[48] in Hamlin
- The Hawley Public Library[49] in Hawley
- The Newfoundland Area Public Library[50] in Newfoundland
- The Northern Wayne Community Library[51] in Lakewood
- The Pleasant Mount Public Library[52] in Pleasant Mount
- The Wayne County Public Library[53] in Honesdale
Seminaries
[edit]There is one seminary, St. Tikhon's Orthodox Theological Seminary[54] in South Canaan.
Communities
[edit]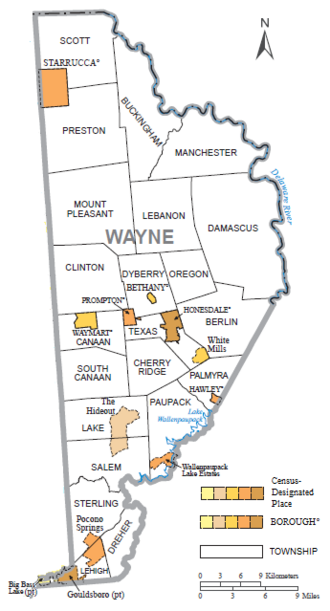
Under Pennsylvania law, there are four types of incorporated municipalities: boroughs, cities, townships, and one town. Wayne County has only boroughs and townships. The latter type is classified based on population by the state government; all of its townships are second-class. A complete list of the county's municipalities follows:
Boroughs
[edit]- Bethany
- Hawley
- Honesdale (county seat)
- Prompton
- Starrucca (established as Wayne Borough in 1853; renamed in 1873)
- Waymart
Townships
[edit]Census-designated places
[edit]In addition, Pennsylvania also has a few types of unincorporated communities, namely villages and private communities. Villages are unincorporated communities within a township, often defined by ZIP code boundaries, property deeds, and local consensus, but which have no official boundaries or population, unless they are also census-designated places (CDPs), geographical areas designated by the US Census Bureau for the purposes of compiling demographic data. Regardless of whether or not they are CDPs, however, they are not actual jurisdictions under Pennsylvania law. Private communities are gated settlements usually governed by a community association, which also often defines the boundaries of the community and may keep track of the number of its members. However, like villages, private communities have no official boundaries or populations, unless they are CDPs, and are never Pennsylvanian jurisdictions. The following is an incomplete list by necessity, but more complete lists of Wayne County's villages and private communities may be found in the corresponding township entry.
- Big Bass Lake (mostly in Lackawanna County)
- Gouldsboro (partially in Monroe County)
- Pocono Springs
- The Hideout
- Wallenpaupack Lake Estates
- White Mills
Unincorporated communities
[edit]Population ranking
[edit]The population ranking of the following table is based on the 2010 census of Wayne County.[55]
† county seat
| Rank | City/Town/etc. | Municipal type | Population (2010 Census) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | † Honesdale | Borough | 4,480 |
| 2 | The Hideout | CDP | 3,013 |
| 3 | Waymart | Borough | 1,341 |
| 4 | Wallenpaupack Lake Estates | CDP | 1,279 |
| 5 | Big Bass Lake (mostly in Lackawanna County) | CDP | 1,270 |
| 6 | Hawley | Borough | 1,211 |
| 7 | Pocono Springs | CDP | 926 |
| 8 | Gouldsboro (partially in Monroe County) | CDP | 890 |
| 9 | White Mills | CDP | 659 |
| 10 | Prompton | Borough | 250 |
| 11 | Bethany | Borough | 246 |
| 12 | Starrucca | Borough | 173 |
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Includes Luzerne, Lackawanna, Monroe, Schuylkill, Carbon, Pike, Wayne, Susquehanna, Wyoming and Sullivan Counties
- ^ "Census - Geography Profile: Wayne County, Pennsylvania". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ a b "Wayne County, PA". Wayne County, PA. Wayne County Courthouse. 2014. Archived from the original on June 30, 2015. Retrieved June 27, 2015.
- ^ Goodrich, Phineas G. (1992) [1880]. History of Wayne County. Baltimore: Gateway Press, Inc.
- ^ a b 2014 Census National Counties Gazetteer File for Pennsylvania (Report). United States Census Bureau. 2014. Retrieved June 27, 2015.
- ^ "PRISM Climate Group at Oregon State University".
- ^ "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 5, 2015.
- ^ "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved August 5, 2015.
- ^ Forstall, Richard L., ed. (March 27, 1995). "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 5, 2015.
- ^ "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. April 2, 2001. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 9, 2022. Retrieved August 5, 2015.
- ^ "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on June 6, 2011. Retrieved August 5, 2015.
- ^ "Census 2020".
- ^ a b c Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data for Wayne County, Pennsylvania (Report). U.S. Department of Commerce. 2010. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved June 27, 2015.
- ^ Selected Economic Characteristics 2009–2013 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates for Wayne County, Pennsylvania (Report). U.S. Department of Commerce. 2013. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved June 27, 2015.
- ^ Occupation by Sex and Median Earnings in the Past 12 Months (In 2013 Inflation-Adjusted Dollars) For the Civilian Employed Population 16 Years and Over 2009–2013 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates for Wayne County, Pennsylvania (Report). U.S. Department of Commerce. 2013. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved June 27, 2015.
- ^ Selected Social Characteristics in the United States 2009–2013 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates for Wayne County, Pennsylvania (Report). U.S. Department of Commerce. 2013. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- ^ "P2 HISPANIC OR LATINO, AND NOT HISPANIC OR LATINO BY RACE – 2020: DEC Redistricting Data (PL 94-171) – Wayne County, Pennsylvania".
- ^ Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ Pennsylvania Department of State (May 15, 2023). "Voter registration statistics by county". dos.pa.gov. Retrieved May 17, 2023.
- ^ Leip, Dave (2012). "2000 Presidential General Election Results - Pennsylvania". Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. David Leip. Archived from the original on November 17, 2015. Retrieved November 15, 2015.
- ^ Leip, Dave (2012). "2004 Presidential General Election Results - Pennsylvania". Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. David Leip. Archived from the original on November 17, 2015. Retrieved November 15, 2015.
- ^ Leip, Dave (2012). "2008 Presidential General Election Results - Pennsylvania". Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. David Leip. Archived from the original on November 17, 2015. Retrieved November 15, 2015.
- ^ Leip, Dave (2012). "2012 Presidential General Election Results - Pennsylvania". Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. David Leip. Archived from the original on September 7, 2015. Retrieved November 15, 2015.
- ^ Leip, Dave (2012). "1964 Presidential General Election Results - Pennsylvania". Dave Leip’s Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. David Leip. Archived from the original on February 29, 2012. Retrieved November 15, 2015.
- ^ "Presidential election of 1892 - Map by counties". geoelections.free.fr. Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ Sullivan, Robert David; ‘How the Red and Blue Map Evolved Over the Past Century’; America Magazine in The National Catholic Review; June 29, 2016
- ^ a b Center, Legislativate Data Processing. "Find Your Legislator". The official website for the Pennsylvania General Assembly. Archived from the original on May 6, 2017. Retrieved May 9, 2017.
- ^ a b c "Commissioners". Wayne County, PA. Wayne County Courthouse. 2014. Archived from the original on December 2, 2014. Retrieved December 17, 2014.
- ^ "Auditors". Wayne County, PA. Wayne County Courthouse. 2014. Archived from the original on December 2, 2014. Retrieved December 17, 2014.
- ^ "Coroner". Wayne County, PA. Wayne County Courthouse. 2014. Archived from the original on December 2, 2014. Retrieved December 17, 2014.
- ^ "District Attorney". Wayne County, PA. Wayne County Courthouse. 2014. Archived from the original on December 2, 2014. Retrieved December 17, 2014.
- ^ "Prothonotary". Wayne County, PA. Wayne County Courthouse. 2014. Archived from the original on December 2, 2014. Retrieved December 17, 2014.
- ^ "Recorder of Deeds". Wayne County, PA. Wayne County Courthouse. 2014. Archived from the original on December 2, 2014. Retrieved December 17, 2014.
- ^ "Register of Wills". Wayne County, PA. Wayne County Courthouse. 2014. Archived from the original on December 2, 2014. Retrieved December 17, 2014.
- ^ "Sheriff". Wayne County, PA. Wayne County Courthouse. 2014. Archived from the original on December 2, 2014. Retrieved December 17, 2014.
- ^ "Treasurer". Wayne County, PA. Wayne County Courthouse. 2014. Archived from the original on December 2, 2014. Retrieved December 17, 2014.
- ^ "Wayne Ambulance - Ambulance Service Area". Archived from the original on March 14, 2014. Retrieved December 2, 2018.
- ^ Writer), Michael Iorfino (Staff (July 29, 2013). "Moses Taylor Hospital acquires Lackawanna Ambulance". thetimes-tribune.com. Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ Cottage Hose Ambulance Employee Manual
- ^ a b Ambulance Company still struggles after fire, Wayne Independence, January 14, 2013
- ^ "Northern Wayne Fire Company - Lakewood, PA". FireDepartment.net. Archived from the original on August 1, 2014. Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ "USP Canaan Contact Information Archived 2010-05-27 at the Wayback Machine." Federal Bureau of Prisons. Retrieved on February 23, 2011. "3057 Easton Turnpike Waymart, PA 18472."
- ^ "Canaan township, Wayne County, Pennsylvania[permanent dead link]." U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved on February 23, 2011.
- ^ "2020 CENSUS - SCHOOL DISTRICT REFERENCE MAP: Wayne County, PA" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved October 31, 2024. - Text list
- ^ "Canaan Christian Academy". Canaan Christian Academy. 2014. Archived from the original on December 19, 2014. Retrieved December 15, 2014.
- ^ "Saint Dominic's Academy". Saint Dominic's Academy. 2013. Archived from the original on December 15, 2014. Retrieved December 15, 2014.
- ^ "Wayne County Pennsylvania Public Libraries". Wayne County Pennsylvania Public Libraries. 2014. Archived from the original on December 15, 2014. Retrieved December 15, 2014.
- ^ "Bethany Public Library Home Page!". Bethany Public Library Home Page!. Archived from the original on December 15, 2014. Retrieved December 15, 2014.
- ^ "Hamlin Community Library". Hamlin Community Library. Wix.com. March 25, 2020. Archived from the original on March 25, 2020. Retrieved March 25, 2020.
- ^ "Hawley Public Library". Hawley Borough. Dynamic Technology Software, Inc. Archived from the original on December 15, 2014. Retrieved December 15, 2014.
- ^ "Newfoundland Area Public Library". Wayne County Pennsylvania Public Libraries. 2014. Archived from the original on December 15, 2014. Retrieved December 15, 2014.
- ^ "Northern Wayne Community Library". Wayne County Pennsylvania Public Libraries. 2014. Archived from the original on December 15, 2014. Retrieved December 15, 2014.
- ^ "Pleasant Mount Public Library". Facebook. Facebook, Inc. November 20, 2014. Retrieved December 15, 2014.
- ^ "Wayne County PA Library". Facebook. Facebook, Inc. December 12, 2014. Retrieved December 15, 2014.
- ^ "Welcome to St. Tikhon's Orthodox Theological Seminary". St. Tikhon's Orthodox Theological Seminary. Retrieved November 16, 2024.
- ^ Promotions, Center for New Media and. "US Census Bureau 2010 Census". www.census.gov. Retrieved April 7, 2018.

